Preventing Data Breaches in E-Waste Recycling
How many sensitive files are floating around in your company? For over 64% of firms, the answer is more than 1,000—accessible to every single employee. Now, think about where those files might end when old devices are retired.
What happens to all that sensitive data when hard drives, printers, and smartphones are tossed out or handed off to third-party recyclers without a second thought?
For Morgan Stanley, the outcome was a nightmare. Decommissioned hard drives containing sensitive client information ended up on an auction site, exposing data from 15 million customers. The breach wasn’t the result of a sophisticated hack but a simple failure to handle e-waste securely.
And it’s not an isolated case. With the average data breach cost exceeding $4.45 million, mishandling e-waste has become a ticking time bomb for businesses.
This blog will explore how improperly handled e-waste leads to breaches and best practices for ensuring your discarded devices don’t become a liability.
How Improperly Handled E-Waste Can Lead to Data Breaches
Many electronic devices retain sensitive data even after they are no longer used. When these devices are improperly recycled or disposed of, their data becomes vulnerable to unauthorized access. Cybercriminals or malicious actors can recover residual data using essential tools and software, exploiting it for identity theft, corporate espionage, or financial fraud.
Improper handling includes failing to sanitize device data, partnering with unverified recycling vendors, and neglecting to secure devices during transport or processing. Without secure processes, e-waste can easily fall into the wrong hands, making data breaches not just a possibility but a probability.
Many electronic devices commonly store sensitive information, making them prime targets for exploitation if not handled securely during disposal. Some examples include:
Hard Drives and Solid-State Drives (SSDs): Even when removed from computers, these storage devices often retain sensitive business data, personal information, and financial records.
Smartphones and Tablets: These devices store contacts, emails, photos, and app data, including banking credentials and other critical applications.
Printers and Copiers: Many modern printers and copiers have internal memory that saves scanned, printed, or faxed documents, which may include highly confidential information.
IoT Devices: Internet of Things (IoT) devices like smart cameras, thermostats, and routers often store network credentials and user data, making them vulnerable to breaches if discarded improperly.
Critical Risks in E-Waste Recycling

While e-waste recycling is essential for sustainability, it poses significant cybersecurity risks if not managed properly. Many electronic devices slated for disposal still contain sensitive or proprietary data, and mishandling these devices can expose organizations to data breaches, regulatory fines, and reputational damage. Here are a few risks associated with e-waste recycling:
Failed Data Destruction
One of the most common and severe risks in e-waste recycling is neglecting to securely erase or destroy data stored on devices. Many organizations mistakenly believe that deleting files or formatting storage devices is sufficient, but this often leaves residual data that can be recovered with specialized tools. Hard drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), smartphones, and printers store sensitive information, from personal identifiers to confidential business records.
These devices can fall into the wrong hands without thorough data sanitization or physical destruction. For instance, improperly wiped devices sold in secondary markets have been found to contain sensitive customer data, trade secrets, and even financial records. Such oversights compromise data security and expose organizations to severe legal and financial consequences.
Inadequate Security Practices
Many organizations rely on third-party vendors to handle their e-waste, but not all vendors prioritize security. Some may lack proper certifications, while others might not adhere to stringent data destruction protocols. Partnering with a vendor that does not implement secure processes for data destruction or device handling significantly increases the risk of data breaches.
For example, unscrupulous vendors may resell devices instead of securely recycling or destroying them, exposing sensitive data. Others may fail to track devices throughout recycling, creating unauthorized access or theft opportunities. Without proper oversight and chain-of-custody protocols, organizations can inadvertently entrust their data to vendors with weak security measures, ultimately compromising their information.
Unauthorized Access
Discarded devices often pass through multiple checkpoints during transport and processing, creating numerous opportunities for unauthorized access. If organizations do not strictly monitor the chain of custody, hackers can intercept devices, steal, or tamper with them before reaching secure facilities.
For example, e-waste transported without secure containers or inventory tracking is vulnerable to theft or loss. Even within recycling facilities, lax security measures allow unauthorized personnel to access devices and retrieve sensitive data. This is particularly concerning for devices containing proprietary information, customer data, or credentials that could be exploited for cyberattacks.
Failing to address these risks can lead to severe consequences, including data breaches, financial losses, regulatory fines, and damage to the organization’s reputation. By recognizing and mitigating the vulnerabilities in e-waste recycling processes, organizations can protect themselves from these potential threats while ensuring compliance with data protection laws.
Best Practices for Preventing Data Breaches in E-Waste Recycling
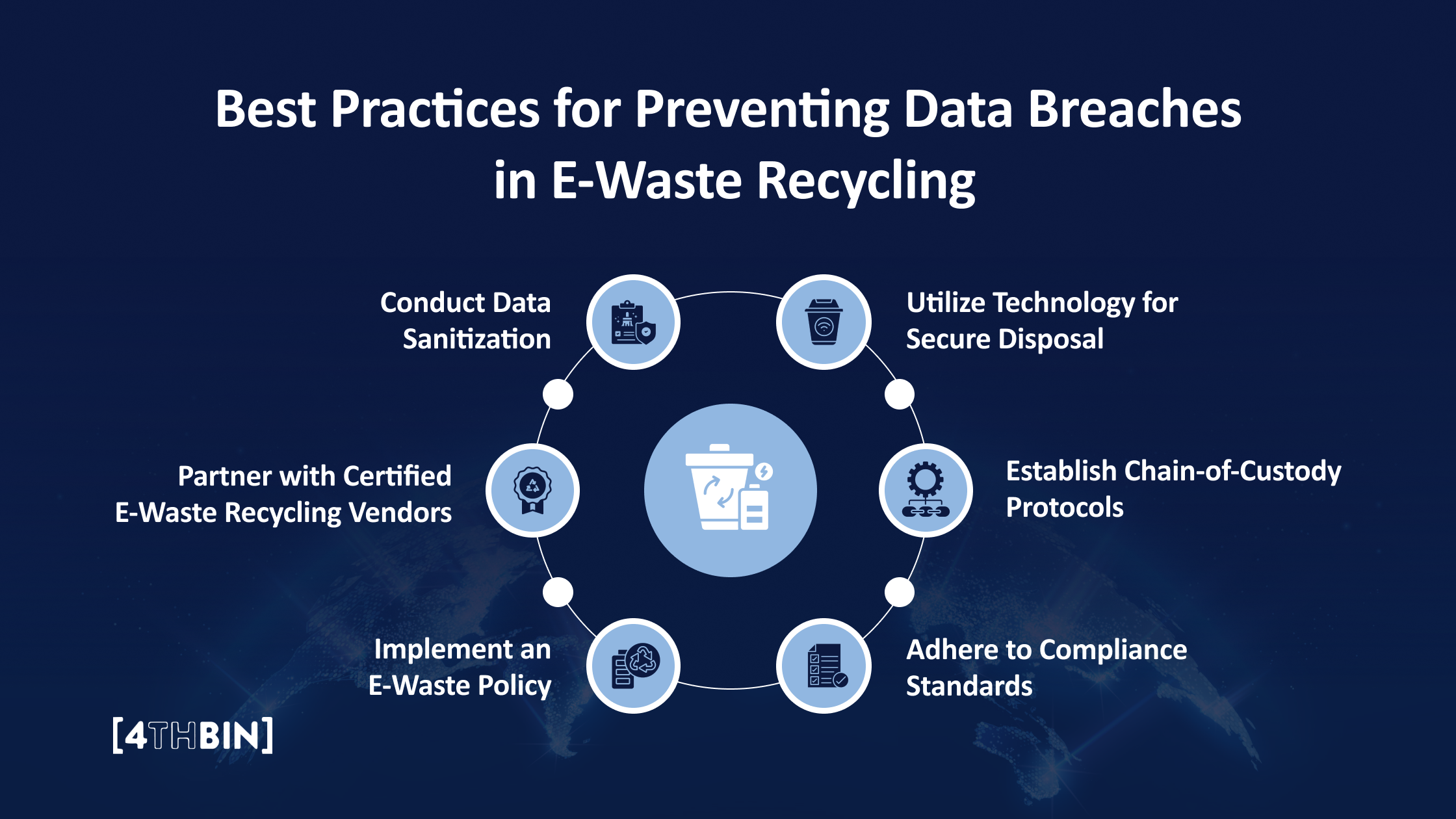
To mitigate these risks, organizations must adopt best practices to ensure that data stored on electronic devices is fully protected throughout the recycling process. Here are the critical measures every organization must take:
Conduct Data Sanitization
One of the most effective ways to prevent data breaches during e-waste recycling is to ensure that all data is thoroughly erased from devices before disposal. This step requires more than just deleting files or formatting storage devices; these methods often leave recoverable data traces.
Organizations must seek the help of e-waste recycling companies, such as 4THBIN, which use certified data-wiping software to overwrite storage devices multiple times, rendering the data irretrievable. For devices containing susceptible information, physical destruction—such as shredding hard drives or using degaussing machines—should be considered to eliminate any possibility of data recovery.
Partner with Certified E-Waste Recycling Vendors
Choosing the right e-waste recycling partner is essential for ensuring secure data handling. Organizations should work exclusively with vendors certified by recognized standards, such as the R2 (Responsible Recycling) or e-Stewards certifications, demonstrating adherence to secure and environmentally friendly recycling practices.
Before partnering with a vendor, conduct thorough due diligence to evaluate their security measures. Look for vendors that provide chain-of-custody documentation, which tracks devices from collection to final processing, ensuring transparency and accountability at every stage. A reputable vendor should also offer on-site destruction services or allow organizations to witness the destruction process to provide additional assurance.
Implement an E-Waste Policy
Establishing a formal e-waste management policy is crucial for creating a consistent approach to data security during device disposal. This policy should outline precise procedures for employees to follow, including:
- Identifying devices eligible for recycling.
- Steps for securely wiping or destroying data before devices leave company premises.
- Guidelines for selecting and working with certified recycling vendors.
Regular training sessions must be conducted to educate employees on the importance of secure e-waste handling and the potential risks associated with improper disposal. A well-informed workforce is the first line of defense against accidental data breaches.
Utilize Technology for Secure Disposal
Advanced technology can significantly enhance data security during e-waste recycling. Encryption is a critical tool that protects sensitive data throughout a device’s lifecycle. By encrypting data at rest, organizations make it significantly harder for unauthorized parties to access information, even if a device falls into the wrong hands before recycling.
Additionally, asset management software can track devices through recycling, ensuring that every piece of equipment is accounted for and securely disposed of. This technology gives organizations a clear view of their e-waste journey, minimizing the risk of lost or misplaced devices.
Establish Chain-of-Custody Protocols
A transparent chain-of-custody process ensures that every device is monitored from when it leaves the organization’s premises until it is securely recycled or destroyed. This protocol reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access or theft during transport and processing.
Organizations must work with vendors who provide detailed documentation at every stage of the e-waste recycling process. This includes tracking serial numbers, maintaining logs of collection and transfer, and issuing certificates of destruction once devices have been securely disposed of. A powerful chain of custody adds a layer of security and accountability to the recycling process.
Adhere to Compliance Standards
Compliance with data protection laws and regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS, is non-negotiable when securing e-waste recycling. These regulations often require organizations to follow specific protocols for data destruction and reporting breaches.
Ensuring compliance involves staying current with applicable laws and integrating their requirements into the organization’s e-waste management policy. By adhering to these standards, organizations reduce their risk of data breaches, avoid regulatory penalties, and demonstrate their commitment to safeguarding sensitive information.
Adopting these best practices is essential for preventing data breaches during e-waste recycling. By taking a proactive approach to secure e-waste recycling, businesses can avoid costly breaches, safeguard their reputations, and ensure the integrity of their data disposal processes.
Keep Your Organizational Data Safe with 4THBIN

With 4THBIN’s certified e-recycling solutions, you can ensure the safety of your data while securely disposing of your outdated electronics.
With over a decade of expertise, 4THBIN has partnered with over 10,000 organizations across the United States, including Fortune 100 companies and startups, to transform e-waste into a valuable resource.
We prioritize data security and environmental impact, ensuring that sensitive information is completely safeguarded with our certified data destruction services. This eliminates the risks of data recovery associated with improper disposal.
Our customizable e-waste recycling solutions include secure RemoteReturn mail-in services and convenient on-site collection options, allowing you to choose a plan that best fits your organization’s needs.
Prevent Data Breaches Before They Happen.
Contact Us










