What Is ESG Reporting? A Comprehensive Guide
You’ve heard the saying, “Numbers don’t lie.”
For decades, companies have measured success primarily through their financial statements, specifically by examining profits, margins, and growth. But in today’s world, that definition of success is evolving.
With over 90% of S&P 500 companies now publishing ESG reports and global sustainable fund assets surpassing USD 600 billion, stakeholders expect more than just financial performance.
Investors, regulators, and consumers now want to understand not just what you earn, but how you earn it. This growing demand for transparency is reshaping global corporate reporting standards.
In the EU, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD); set to take effect in 2025, marks a pivotal shift from voluntary to mandatory ESG reporting requirements.
ESG reporting is no longer a corporate trend; it has become the foundation of responsible, transparent, and sustainable business. Whether you’re a startup seeking investor trust or a global enterprise preparing for compliance, mastering ESG reporting is now a strategic necessity.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know.
What Does ESG Stand For?
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance: three pillars that measure how responsibly an organization operates beyond financial performance. Together, they form the foundation for credible ESG reports.
Environmental (E)
Assesses a company’s impact on the planet through metrics like:
- Carbon emissions and energy efficiency
- Water usage and waste management
- Renewable energy adoption
- Sustainable supply chain initiatives
Example: Apple powers all global operations with 100% renewable energy and aims to achieve a fully carbon-neutral supply chain by 2030.
Social (S)
Examines how a company treats its employees, customers, and the communities it serves.
- Fair labor practices and safe working conditions
- Diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) programs
- Community engagement and social responsibility
- Customer data protection and product safety
Example: Starbucks publicly shares DEI metrics and supports ethical coffee sourcing programs in developing regions.
Governance (G)
Focuses on leadership ethics and transparency.
- Board diversity and accountability
- Executive pay alignment with sustainability goals
- Anti-bribery and corruption controls
- Transparent decision-making and auditing
Example: Unilever links executive bonuses directly to sustainability and inclusion KPIs.
What Is ESG Reporting?
ESG reporting is the structured process of measuring, analyzing, and disclosing a company’s performance across environmental, social, and governance (ESG) dimensions.
It converts sustainability efforts into standardized, data-driven insights, showing stakeholders how responsibly and effectively a business operates.
ESG reporting answers three critical questions:
- What impact are we creating on people and the planet?
- How are we managing those impacts?
- What are our goals for continued improvement?
Unlike narrative-driven CSR reports, ESG reports are quantitative, verifiable, and comparable, making them essential tools for investors, regulators, and partners.
Significance of ESG Reporting
Investor Expectations
The financial world is undergoing a shift: investors aren’t only chasing returns anymore; they’re scrutinizing how value is created. ESG metrics have become a critical lens into risk, resilience, and long-term legitimacy.
- According to Bloomberg Intelligence, ESG-aligned assets are expected to exceed USD $40 trillion by 2030. Investors now benchmark companies based on ESG reporting metrics, assessing their long-term value, risk, and resilience.
- In the EY 2024 Institutional Investor Survey, 88% of institutional investors said they’ve increased their use of ESG information in recent years, showing that ESG is no longer a fringe consideration.
- However, the survey also revealed tension: 92% of investors believe ESG initiatives may harm short-term performance, highlighting the balance they try to strike between financial returns and sustainability goals.
Why does this matter for the companies?
- To attract capital, your ESG credentials must be provable, not aspirational.
- Investors use ESG disclosures to benchmark, compare, and de-risk their portfolios; therefore, weak or opaque ESG reporting can be a significant competitive disadvantage.
- As capital increasingly flows toward “sustainable” or “ESG-integrated” funds, companies lacking credible ESG data risk being left behind.
Regulatory Compliance
Globally, regulators are no longer waiting; they are writing the rules. ESG reporting is shifting from voluntary to mandatory in many jurisdictions.
- In the European Union, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) requires many companies to integrate sustainability disclosures into their financial reporting, with external assurance and standardized ESG data.
- In India, the Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR) is mandatory for the top 1,000 listed companies, requiring in-depth ESG disclosures, including governance, environmental impact, and social initiatives.
- In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is advancing rules that would require companies to disclose climate-related risks, including greenhouse gas emissions and the oversight of their boards.
Why must companies care?
- Noncompliance can invite penalties, delisting risks, or reputational damage.
- ESG laws often include audit/assurance mandates, meaning data must meet verification and quality standards.
- Regulatory regimes are converging: cross-border firms may need to satisfy multiple regional ESG rules, making alignment and integration critical.
Brand Trust & Reputation
Transparency on social, environmental, and governance issues is increasingly seen by stakeholders (customers, employees, regulators) as a trust litmus test.
- Strong ESG and sustainability reporting enhances brand credibility. Transparent data demonstrates accountability and prevents greenwashing, enabling businesses to earn trust from consumers, employees, and regulators.
- For employees, a clear commitment to ESG can boost morale, retention, and attract talent who prioritize purpose over pay.
- NGOs, the media, and civil society now closely monitor ESG claims. Weak or inconsistent disclosure invites accusations of greenwashing, which can erode credibility faster than outright failure.
Operational Efficiency
ESG reporting isn’t just external facing; internally, it can reveal inefficiencies and cost leaks that typically go unnoticed.
- Energy audits tied to emissions tracking often reveal waste in lighting, HVAC systems, or production lines, resulting in significant cost savings.
- Supply chain disclosures may expose suppliers to compliance or labor issues, prompting them to switch to more reliable or ethical partners.
- Data from ESG metrics often helps root out duplication across departments (e.g., procurement, waste management, logistics), encouraging more streamlined processes.
In short, ESG reporting forces organizations to view themselves in a new light, identifying latent inefficiencies that traditional financial analysis might overlook.
Long-Term Resilience
ESG disclosures serve as an early warning system, helping companies detect shifts in environment, society, regulation, or governance before risks become crises.
- Climate scenarios, social unrest, or regulatory changes that once seemed distant can manifest suddenly. Well-structured ESG reporting helps you stress-test strategies against such shocks.
- Companies with strong ESG track records tend to recover more quickly in downturns; for instance, in volatile markets, “sustainable” funds often demonstrate greater resilience.
- An ESG-aligned strategy encourages future-readiness in firms that embed sustainability into their core operations, positioning them better for systemic transitions (e.g., carbon pricing, new regulations, and shifting consumer expectations).
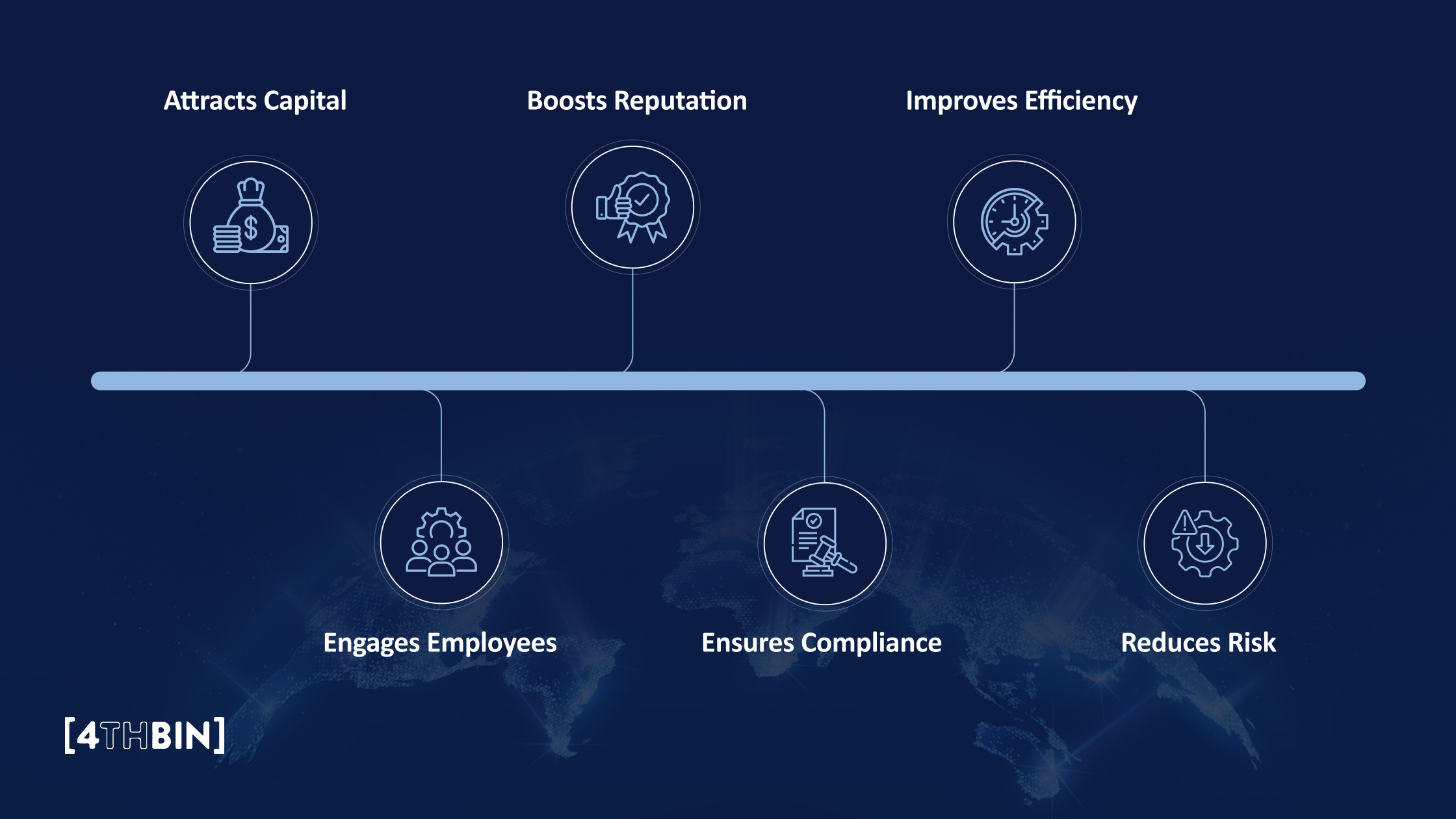
6 Benefits of ESG Reporting
- Attracts Capital: Investors, both institutional and impact-focused, actively seek companies with credible ESG metrics. Strong ESG disclosure helps your organization stand out to these investors and can unlock access to ESG-focused funds or sustainable financing instruments such as green bonds.
- Boosts Reputation: Transparent ESG reporting signals accountability and integrity. Brands that communicate their environmental, social, and governance efforts openly tend to gain the trust of consumers, regulators, and advocacy groups. A well-crafted ESG report can even turn skeptics into supporters, strengthening your brand image.
- Improves Efficiency: When companies track and analyze factors like energy use, emissions, waste, and resource consumption, they often uncover inefficiencies or redundancies that might otherwise go unnoticed. ESG measurement drives continuous improvement, helping businesses reduce costs and operate more sustainably.
- Engages Employees: Employees are more motivated when they see their company committed to values beyond profit. Whether it’s supporting community initiatives, promoting diversity, or pursuing environmental goals, these efforts help employees feel part of a meaningful mission. The result is higher engagement, stronger loyalty, and lower turnover.
- Ensures Compliance: Adhering to ESG frameworks keeps your organization aligned with emerging regulations and disclosure mandates. Proactive ESG alignment not only prevents legal and reputational risks but also ensures your company stays ahead of evolving reporting requirements.
- Reduces Risk: ESG reporting allows organizations to identify and address potential vulnerabilities early, whether they relate to labor conditions in the supply chain, climate risks, or governance lapses. By addressing minor issues before they escalate, businesses can prevent costly disruptions and maintain long-term stability.
The Overlooked Factor: E-Waste in ESG Reporting
When businesses consider sustainability, they often focus on renewable energy, emissions, or water use; however, e-waste (electronic waste) remains one of the most overlooked metrics in ESG reporting.
Every year, the world generates over 62 million metric tons of e-waste; less than a quarter of this waste is formally recycled. The rest ends up in landfills or informal dumps, releasing toxic substances such as lead, mercury, and brominated plastics that harm both ecosystems and human health.
The irony? E-waste is one of the easiest sustainability wins when handled responsibly. It directly impacts two pillars of ESG:
- Environmental: Proper IT asset disposal reduces greenhouse-gas emissions by recovering reusable metals (like copper and gold) and minimizing the need for raw-material mining.
- Governance: Every hard drive, laptop, or server holds sensitive data. Secure data destruction during e-waste recycling ensures compliance with privacy laws (such as GDPR and HIPAA) and protects a company's reputation.
Neglecting e-waste management doesn’t just harm the planet; it also exposes organizations to data security, compliance, and reputational risks that can weaken ESG scores.
Best Practices for Including E-Waste in ESG Reports
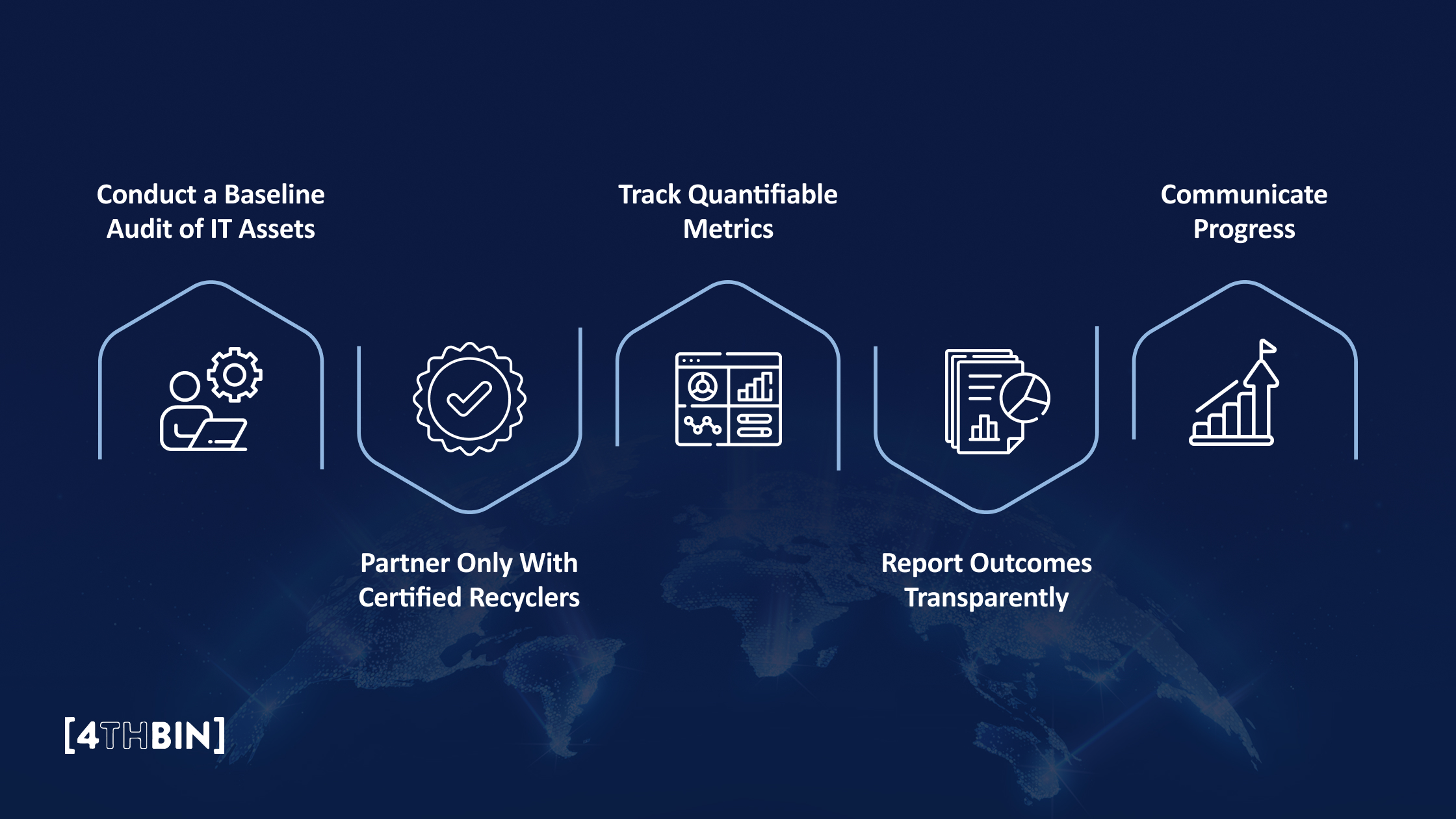
Companies aiming to integrate e-waste into their ESG frameworks should follow a structured, auditable approach.
Conduct a Baseline Audit of IT Assets: Start by inventorying your active, inactive, and end-of-life IT assets. Identify which can be reused, refurbished, or securely recycled.
Partner Only With Certified Recyclers: Work exclusively with R2v3 or e-Stewards certified recyclers. These certifications ensure environmentally sound handling, worker safety, and the complete destruction of all data.
Track Quantifiable Metrics: Collect measurable data points for your ESG disclosures:
- Total weight of e-waste recycled (in kilograms or tons).
- Volume of materials recovered (copper, aluminum, plastics).
- Estimated carbon offset from reuse or recycling.
- Number of data destruction certificates issued.
Report Outcomes Transparently: Integrate e-waste data into your ESG or sustainability report under the Environmental (resource recovery, emissions saved) and Governance (data protection compliance) sections. Ensure third-party verification to validate impact and enhance investor confidence.
Communicate Progress: Showcase these outcomes publicly through sustainability dashboards, annual reports, or case studies, to position your brand as both digitally responsible and environmentally accountable.
E-waste is one of the fastest-growing waste streams in the world, yet one of the most manageable through structured, responsible action.
By incorporating e-waste metrics into ESG reporting, companies not only reduce carbon emissions but also demonstrate accountability, transparency, and technological ethics.
With partners like 4THBIN, organizations can transform what was once an environmental liability into a measurable ESG asset, thereby strengthening their scores, investor trust, and long-term sustainability credibility.
Empower Your ESG Impact with 4THBIN
Building a sustainable business starts with transparency. ESG reporting and responsible technology management go hand in hand; both ensure that what powers your organization today supports a cleaner, fairer tomorrow.
At 4THBIN, we help companies strengthen their ESG performance through certified e-recycling solutions, secure data destruction, and measurable environmental impact. Every device recycled and every report disclosed contributes to a future where progress and responsibility move hand in hand.
When you partner with 4THBIN, you’re not just meeting compliance, you’re leading the way in accountability, innovation, and sustainability.
Take the next step. Contact us to align your ESG goals with responsible e-recycling and make your impact count.