What Is A Green Data Center? Everything You Need to Know
A decade ago, data centers were a growing part of global infrastructure.
Today, they are the foundation of the digital world. With cloud computing, AI workloads, streaming, and nonstop data storage needs, facilities are expanding at record speed.
Hyperscale data centers alone are expected to surpass 1,000 sites by 2026.
This growth comes with severe environmental pressure. Data centers now consume about 2% of global electricity, nearly equal to the aviation sector, and analysts warn that number could double within the decade if efficiency doesn’t improve.
Water usage is another concern. Many large data centers consume millions of gallons of water per day for cooling, straining already limited regional water resources. On top of that, constant hardware refresh cycles generate massive e-waste, increasing the need for responsible recycling and material recovery.
These realities are driving a shift toward green data centers developed to reduce energy use, lower emissions, conserve water, and extend the lifecycle of IT equipment through reuse and certified recycling. The mission is simple: support digital growth without sacrificing environmental responsibility.
In this blog, we’ll break down what green data centers are, why they matter for ESG and business resilience, and how organizations can take meaningful steps toward sustainability with support from responsible partners like 4THBIN.
What Is a Green Data Center?
A green data center is a facility that uses energy-efficient equipment, sustainable infrastructure, renewable power sources, and responsible recycling practices to reduce its environmental impact.
Green data centers prioritize:
- Lower energy consumption & smarter power distribution
- Efficient cooling strategies to reduce reliance on traditional HVAC
- Renewable energy, including solar, wind, and hydro
- Hardware reuse & certified recycling at end-of-life
- Transparent reporting on sustainability performance
- Circular resource strategies that extend the life of technology
Instead of discarding outdated servers or devices, sustainable practices ensure components can be refurbished, repurposed, or responsibly recycled, with valuable materials recovered before disposal.
Significance of Green Data Centers
The rapid growth of cloud services, AI workloads, and global data consumption has put enormous pressure on traditional data center models. Energy demand is soaring, e-waste volumes are increasing, and sustainability expectations are higher than ever.
Organizations can no longer treat data infrastructure as an invisible backend system. How data is stored, powered, cooled, and ultimately retired has become directly tied to ESG performance, operational efficiency, and brand trust.
Green data centers have emerged as a strategic answer to these pressures, combining energy-efficient design, renewable power, optimized resource use, and responsible hardware lifecycle management. Their significance extends far beyond environmental benefits. For many companies, they are quickly becoming a competitive differentiator.
Here’s why green data centers matter today more than ever.
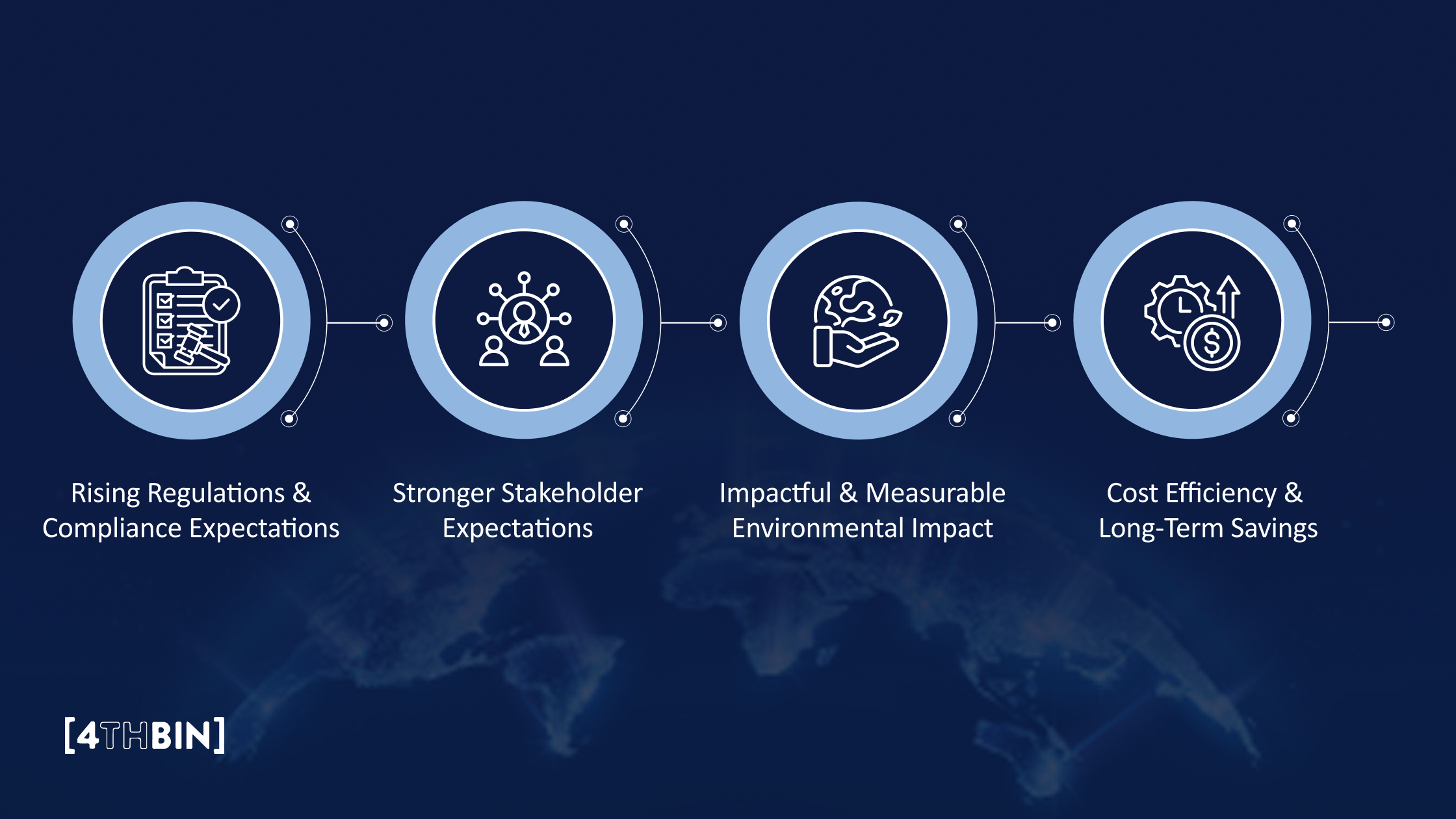
Rising Regulations & Compliance Expectations
Regulatory pressure is growing globally. For example, the European Commission has proposed a Data Centre Energy Efficiency Package that aims to make data centers “climate-neutral, energy-efficient and sustainable” by 2030.
Meanwhile, laws targeting electronic waste, like the WEEE Directive in the EU, require responsible collection, recycling, and recovery of discarded electronics, making certified e-waste handling a legal and environmental necessity.
As governments tighten standards on carbon emissions, energy use, and waste disposal, organizations with in-house or outsourced data infrastructure are increasingly accountable for the environmental impact of their digital footprint.
Stronger Stakeholder Expectations
Large tech companies are already leading by example. Google operates data centers powered primarily by renewable energy and aims to achieve 24/7 clean-energy consumption in many regions.
Similarly, Microsoft has committed to running its data centers on 100% renewable energy, part of a broader push to meet sustainability and carbon-neutrality goals.
As customers, investors, and regulatory bodies increasingly scrutinize ESG credentials, companies that cannot demonstrate sustainable data center practices may face reputational, financial, or compliance risks. Stakeholder demand for transparent, verifiable ESG performance is real and growing.
Impactful & Measurable Environmental Impact
Data centers contribute significantly to global energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. A study notes that data centers now account for about 3% of global electricity demand and roughly 2% of global greenhouse-gas emissions.
Green data centers translate directly into lower emissions and reduced waste, whether through renewable energy adoption, efficient cooling, higher hardware utilization, or certified recycling. These reductions are tangible, measurable, and often visible within months, not years.
As more companies adopt circular hardware management, reusing, recycling, or refurbishing IT assets, the cumulative effect can be substantial: lower resource extraction, less landfill waste, and reduced carbon footprint across entire supply chains.
Cost Efficiency & Long-Term Savings
- Energy efficiency and optimized resource usage reduce operating expenses over time. Facilities that use advanced cooling systems, maximize server utilization, or rely on renewable power are less vulnerable to volatile energy prices.
- Consolidation of workloads, using fewer physical servers through virtualization or workload balancing, significantly cuts power and maintenance needs. Research shows many traditional data center environments under-utilize servers, with up to 30% consuming power while doing little or no practical work.
- Hardware reuse and certified recycling reduce capital costs: instead of constantly buying new devices, companies can extend hardware lifecycles, recover material value, and minimize total cost of ownership when equipment retirement is managed responsibly.
Core Components of Green Data Centers
Building a truly green data center requires more than switching to cleaner power. It involves rethinking how infrastructure is planned, operated, cooled, monitored, and eventually retired.
Sustainable performance comes from integrating energy-efficient systems, renewable power sources, and responsible end-of-life management for hardware. The following elements form the backbone of modern green data center strategy:
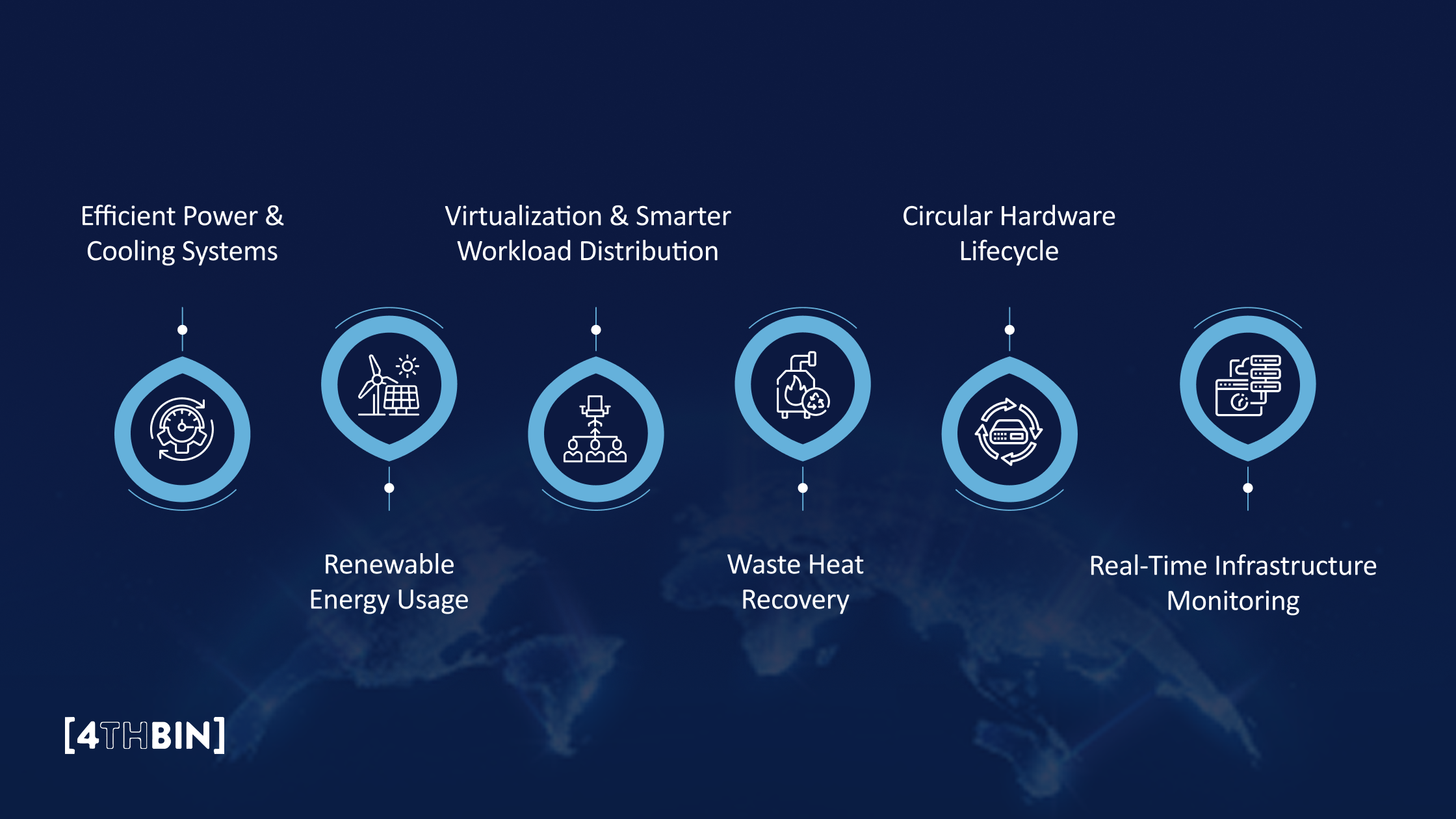
Efficient Power & Cooling Systems
Heat management is one of the most resource-intensive aspects of traditional data centers. Historically, facilities relied heavily on large-scale air conditioning, consuming enormous amounts of electricity just to keep hardware from overheating. Green data centers use advanced alternatives, including liquid cooling, free-air cooling, and hot-aisle or cold-aisle containment to strategically control airflow.
Some facilities even use intelligent, sensor-driven airflow automation to maintain optimal temperature with minimal energy. These innovations drastically reduce strain on power systems and improve equipment performance and longevity.
Renewable Energy Usage
Switching from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower significantly reduces carbon emissions. Many hyperscale providers are already making the shift. For example, several Google Cloud and AWS regions now operate on 100 percent renewable energy, demonstrating what is possible at scale. Power purchase agreements and on-site solar installations are becoming common strategies for companies working toward net-zero goals.
Virtualization & Smarter Workload Distribution
Virtualization technology allows multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server, increasing hardware utilization and reducing the total number of machines required. This means less energy consumed, fewer devices manufactured, and a lower overall footprint. Bright workload orchestration and automation also ensure that computing power is allocated only when needed, reducing idle energy waste.
Waste Heat Recovery
Instead of releasing excess heat into the environment, sustainable data centers repurpose it. In Finland and Sweden, for example, data centers are already supplying recovered heat to municipal district heating systems, providing warmth to tens of thousands of homes. This approach turns a byproduct into a valuable energy resource and contributes to community sustainability.
Circular Hardware Lifecycle
Supporting green operations isn’t just about power; it’s also about the responsible handling of physical equipment. Green data centers extend the lifecycle of servers and components through refurbishment, reuse, and responsible recycling. Partnering with certified IT asset recovery and recycling providers ensures that valuable materials such as aluminum, copper, silver, gold, and rare earth metals are recovered rather than sent to landfills, reducing the environmental and social burden of mining.
Real-Time Infrastructure Monitoring
Modern data centers rely on sophisticated infrastructure management platforms that provide real-time visibility into power consumption, cooling efficiency, performance, and capacity. By continuously tracking usage, operators can rapidly identify waste, proactively adjust environments, and prevent failures before they occur. This transforms efficiency from a one-time initiative into a continuous improvement cycle.
How Green Data Centers Support ESG Goals
Sustainable data centers deliver measurable value across all three pillars of ESG, making them among the most practical and high-impact levers for organizations seeking to strengthen sustainability performance and transparency.
1. Environmental Impact
Green data centers dramatically reduce energy consumption by using efficient cooling, renewable power, and more innovative computing strategies. They also minimize e-waste through circular hardware practices that extend device lifecycles and recover valuable materials at end-of-life. This approach lowers greenhouse gas emissions, reduces reliance on natural resource extraction, and creates a smaller physical and carbon footprint.
2. Social Responsibility
When data centers operate sustainably, they reduce demand for mining raw materials and the spread of hazardous waste into landfills, soil, and community environments. Responsible recycling and safe handling of e-waste support public health and demonstrate accountability to the communities where organizations operate. Many companies now view sustainable infrastructure as a direct reflection of their values and social impact commitments.
3. Governance and Transparency
Modern ESG reporting frameworks require traceable, verifiable data, and green data centers support that need through auditable documentation across asset lifecycles. From material recovery records to emissions reporting, accountable recycling practices build trust with regulators, investors, partners, and customers. Evident reporting strengthens compliance readiness and protects the brand reputation at a time when sustainability claims are closely scrutinized.
As organizations move toward verifiable ESG performance, the ability to measure, document, and report recycling outcomes is becoming essential rather than optional. This is where expert partners like 4THBIN play a critical role in enabling secure, compliant, and environmentally responsible technology operations.
4THBIN’s Role in Supporting Green Data Center Sustainability
Energy efficiency is only part of the equation. A truly green data center must also manage end-of-life equipment responsibly. The moment servers, storage systems, or networking hardware reach the end of their lifespans, decisions about disposal significantly impact sustainability outcomes.
This is where 4THBIN helps.
As a certified e-recycler and IT asset disposition and recovery programs, we ensure that all retired equipment is processed securely and sustainably through certified recycling and reuse programs.
4THBIN services that support green data center operations include:
- Certified data destruction services that eliminate risk and meet security and compliance standards
- IT asset disposition and recovery programs that maximize reuse and material recovery value
- RemoteReturn solutions for distributed and multi-location infrastructure
- Responsible recycling that diverts e-waste from landfills and recovers critical resources
- Transparent reporting to support sustainability goals and ESG disclosures
With over 10,000 clients and millions of pounds of electronics recycled securely, 4THBIN has helped organizations reduce environmental impact while maintaining the highest standards of data protection and compliance.
Why Green Data Centers Represent the Future
As sustainability commitments grow stronger, responsible digital infrastructure is quickly becoming a cornerstone of corporate transformation. Green data centers support long-term operational goals, including:
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Lower resource consumption and waste
- Responsible supply chain and lifecycle transparency
- Better ESG ratings and investment appeal
- Resilience against future sustainability regulations
Organizations that adopt circular technology strategies today will be better positioned for tomorrow’s regulatory and environmental landscape.
Take the First Step Toward a Greener Data Future with 4THBIN
Green data centers are essential to reducing environmental impact, but sustainability does not end when equipment stops running. Responsible IT asset retirement protects sensitive information while ensuring valuable materials are recovered and recycled.
4THBIN partners with companies ready to integrate sustainability into every stage of the technology lifecycle and build a greener, more responsible digital future.
If you are ready to strengthen your ESG recycling practice, our team is here to help you take the next step.
Partner with 4THBIN today to create a technology lifecycle strategy that supports business growth and environmental accountability.