The Ultimate Guide to E-Waste Management
Think about it – What’s hiding in your storage closets, basements, or office storerooms? Old laptops, unused chargers, or obsolete servers? Chances are, you’re holding onto items that aren’t just clutter; they’re part of a growing global crisis.
We generate more than 40 million tons of electronic waste yearly, which is like throwing 800 laptops every second. Yet only 17% of this waste is recycled correctly. The rest piles up in landfills, leaching toxic chemicals like mercury and lead into the environment or being illegally exported to countries with little capacity to manage it safely.
But here’s the catch — e-waste isn’t just trash. Inside those discarded electronics are $62.5 billion of recoverable materials—gold, copper, silver, and rare earth metals—that could fuel a more sustainable economy. Instead, these valuable resources are wasted, contributing to environmental degradation and a massive missed opportunity for businesses and individuals alike.
With projections estimating that e-waste will hit 74 million metric tons by 2030, addressing this issue has never been more urgent.
This guide will discuss e-waste management, its importance, types of e-waste, approaches to e-waste management, general guidelines for e-waste disposal, and why businesses must partner with certified e-waste recyclers.
What is E-Waste Management?
E-waste management is all about responsibly dealing with old or unwanted electronics like computers, smartphones, printers, TVs, and other gadgets we no longer use. With technology advancing so quickly, devices often become outdated or break down, creating a growing pile of electronic waste—one of the fastest-growing waste streams in the world.
But e-waste isn’t just any kind of trash. It contains valuable materials like gold, silver, copper and harmful substances like lead and mercury. Therefore, managing it properly is essential for the environment and our health.
Why is E-Waste Recycling Crucial?
E-waste recycling offers numerous benefits beyond simply disposing of old devices. Here’s a closer look at why recycling e-waste is so essential:
Protects the Environment
Electronic waste contains various hazardous substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium. When electronics are thrown away carelessly, these toxic materials can seep into the soil and water, polluting ecosystems and threatening wildlife. Recycling ensures that these harmful components are safely extracted and managed, preventing the long-term environmental impact of e-waste.
Recovers Valuable Resources
Electronics contain valuable materials, including precious metals like gold and silver and essential industrial elements like copper and rare earth metals. The material value of used electronic devices is $62.5 billion annually, three times more than the annual output of the world’s silver mines. Instead of letting these resources go to waste, recycling recovers them for reuse. This reduces the demand for destructive mining practices and preserves finite resources for future generations.
Reduces Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Mining, refining, and manufacturing new materials are energy-intensive processes significantly contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Recycling e-waste reduces the need for these processes. For example, recovering metals from old electronics uses far less energy than extracting them from ore, helping to combat climate change and lower our carbon footprint.
Promotes a Circular Economy
One of the most exciting benefits of e-waste recycling is its role in building a circular economy. By recovering materials from discarded electronics and reintroducing them into the production cycle, we reduce waste and minimize the need for new resources. This approach supports sustainable manufacturing and encourages more efficient use of materials.
Protects Public Health
Improper disposal of e-waste can have serious health consequences. Toxic chemicals released into the air, water, and soil can cause respiratory issues, neurological disorders, and other health problems for nearby communities. Recycling ensures that these hazardous components are safely handled, reducing the risk of exposure and protecting public health.
Ensures Data Security
Many electronic devices, such as computers, smartphones, and tablets, store sensitive personal or business data. Throwing these devices away without proper data destruction poses a significant risk of identity theft or data breaches. Certified e-waste recyclers use secure processes to erase or destroy data, safeguarding your information and ensuring data security.
Drives Innovation and Job Creation
E-waste recycling is good for the planet and the economy. The industry creates jobs in collection, dismantling, refurbishment, and materials recovery. A study reveals that if 100% of e-waste is recycled, it would create over 1,700 jobs. Additionally, the growing need for more efficient recycling technologies drives innovation, making it a growing sector with long-term potential.
Types of E-Waste & How to Dispose It?
E-waste includes various discarded electronic devices and components. Understanding these categories and disposing of them responsibly helps protect the environment and conserve resources. Here are the common types and how to handle them:
- Large Household Appliances
Examples include refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners. You can dispose of them through manufacturer or retailer take-back programs, certified e-waste recycling centers, or municipal bulk recycling services.
- Small Household Electronics
Devices like toasters, coffee makers, and microwaves should be dropped off at local recycling centers or collection drives. Functional items can be donated to extend their lifecycle.
- Consumer Electronics
Smartphones, laptops, tablets, and televisions can often be traded through manufacturer programs or recycled via certified facilities. Donate working devices to organizations for refurbishment and reuse.
- Office Equipment and IT Devices
Computers, printers, and servers should be handled by certified e-waste recyclers that offer secure data destruction. Functional equipment can be donated to nonprofits or used by businesses for IT asset disposition services.
- Batteries
Dispose of lithium-ion, lead-acid, and rechargeable batteries at designated recycling locations or hazardous waste facilities. Avoid throwing them in the trash due to environmental risks.
- Lighting and Electrical Equipment
Items like LED lights and fluorescent tubes, especially mercury-containing materials, should be recycled at specialized facilities or hazardous waste drop-off centers.
- Medical and Laboratory Equipment
Devices such as thermometers and X-ray machines must be recycled through certified facilities that comply with hazardous materials regulations. Working equipment can be refurbished for donation or resale.
- Cables, Wires, and Accessories
USB cables, chargers, and power cords can be recycled at e-waste centers, where valuable materials like copper can be recovered. Some retailers also accept these items for recycling.
- Industrial and Commercial Electronics
Machinery controllers and telecommunications systems require disposal through specialized industrial e-waste recyclers. Many manufacturers offer take-back or end-of-life services to meet regulatory standards.
Approaches to E-Waste Recycling
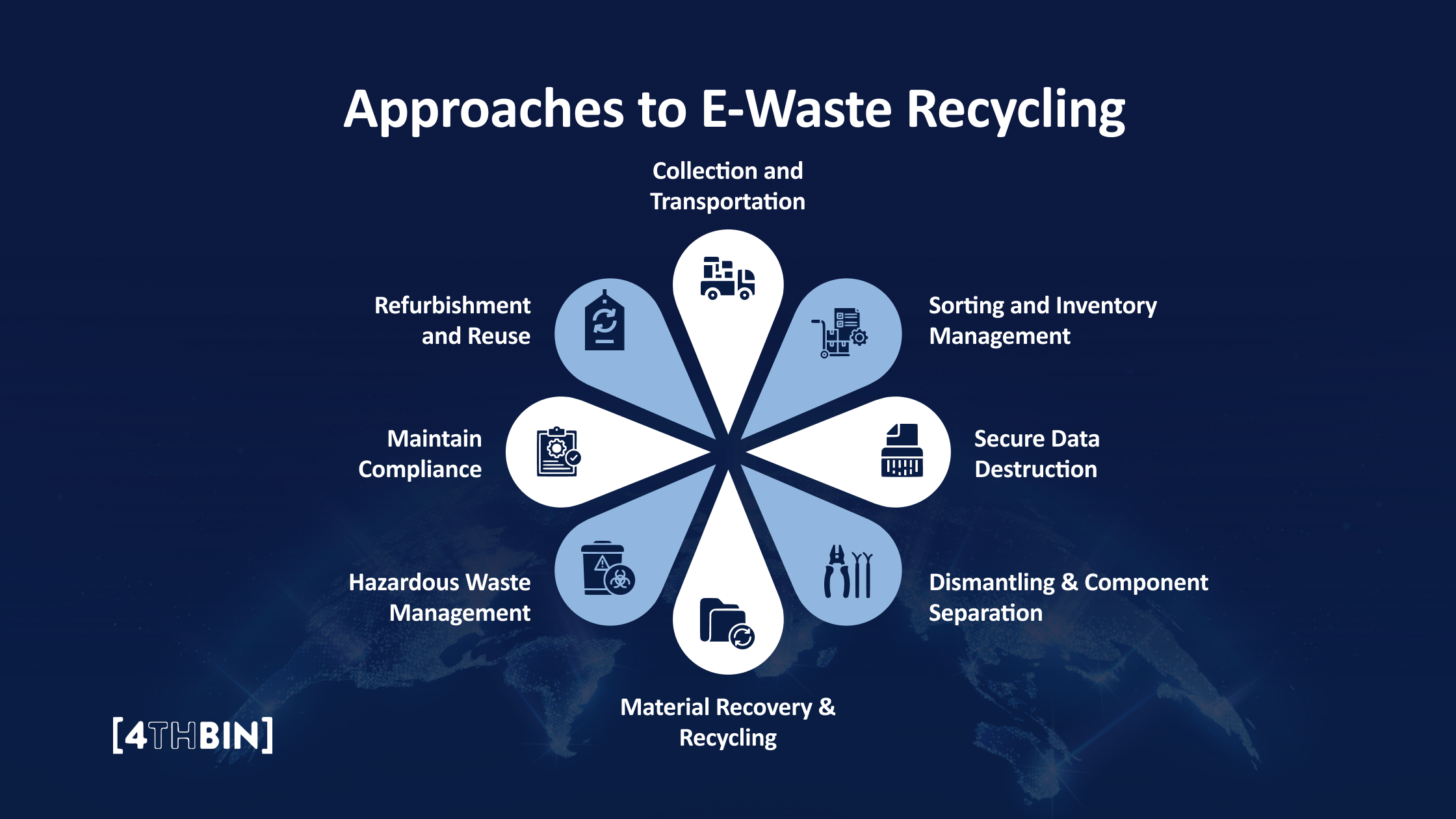
E-waste recycling involves processes that safely and efficiently manage discarded electronics while recovering valuable materials and reducing environmental harm. Certified recyclers follow stringent standards to ensure ethical and sustainable recycling practices. Here is how they manage and recycle e-waste effectively:
Collection and Transportation
The first step in e-waste recycling is collecting discarded electronics. Certified recyclers partner with businesses, organizations, and individuals to collect devices through drop-off centers, collection drives, or pick-up services. Once collected, the e-waste is transported to recycling facilities in compliance with safety and regulatory requirements.
Sorting and Inventory Management
At the recycling facility, the e-waste is sorted into categories based on material composition, device type, and condition. Functional devices may be sent for refurbishment or resale, while non-functional items are processed further. An inventory is created to track the materials and ensure proper handling.
Secure Data Destruction
Computers, smartphones, and servers often contain sensitive personal or corporate data. Certified recyclers prioritize secure data destruction using methods like:
Data Wiping: Overwriting data multiple times to render it unrecoverable.
Hard Drive Shredding: Physically destroying storage devices to prevent unauthorized access.
Degaussing: Using magnetic fields to erase data on drives and tapes.
These data destruction processes ensure compliance with data privacy regulations and eliminate the risk of data breaches.
Dismantling & Component Separation
E-waste is manually or mechanically dismantled to separate different components, such as:
- Metals: Copper, aluminum, steel, and precious metals like gold and silver.
- Plastics: Recyclable polymers for manufacturing new products.
- Glass: Screens and cathode ray tubes (CRTs) for reuse in construction or new electronics.
- Hazardous materials: Batteries, mercury, and lead-containing parts for safe disposal.
This separation ensures that each material is handled appropriately for recovery or disposal.
Material Recovery & Recycling
Once separated, recyclable components undergo specialized processes:
Metals recovery: Smelting or chemical treatment to extract valuable metals.
Plastic processing: Shredding and melting to create pellets for reuse in new products.
Glass recycling: Crushing and cleaning to produce new screens or construction materials.
Certified recyclers use environmentally friendly methods to maximize recovery rates while minimizing energy use and emissions. Several e-waste recycling companies, such as 4THBIN, offer specialized programs such as the silver recovery program to extract silver from medical equipment safely and efficiently.
Hazardous Waste Management
Toxic materials such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and certain chemicals are isolated during dismantling. These materials are treated in compliance with environmental regulations, ensuring they do not pollute soil, water, or air. Certified recyclers employ proper containment and disposal methods, such as encapsulation or chemical neutralization, to prevent these hazardous substances from affecting the environment and human health.
Maintain Compliance
Certified recyclers adhere to international and industry standards, such as:
- R2v3 (Responsible Recycling): Emphasizes environmental responsibility, data security, and worker safety.
- e-Stewards Certification: Focuses on ethical recycling and preventing e-waste exports to developing countries.
- ISO 14001: Ensures adherence to environmental management systems.
These certifications guarantee that recyclers follow best practices for sustainable and responsible e-waste management.
Refurbishment and Reuse
Devices and components in working condition are repaired, refurbished, or upgraded for resale or donation. Refurbishment extends electronics’ lifespans, reduces waste, and provides underserved communities access to affordable technology.
By partnering with certified recyclers, businesses and individuals can ensure their e-waste is managed responsibly, contributing to environmental sustainability, resource conservation, and a safer planet for future generations.
General Guidelines for E-Waste Disposal
Proper e-waste disposal is essential to minimize environmental harm, conserve resources, and protect public health. Whether you’re an individual clearing out old devices or a business managing large volumes of obsolete equipment, following these guidelines ensures your e-waste is handled responsibly:
Check Local Laws & Programs
E-waste regulations vary widely by region. Some areas have strict laws requiring responsible disposal, while others offer free collection services or recycling events. Both businesses and individuals should familiarize themselves with local rules to avoid fines and ensure compliance. Many municipalities provide drop-off locations, scheduled pick-ups, or designated recycling days for electronics. For businesses, partnering with certified e-waste recycling companies can simplify compliance with these regulations.
Choose Certified Recyclers
Not all recyclers are equal. Look for certified e-waste recyclers that meet standards like R2v3 or e-Stewards, which ensure ethical and environmentally safe processing. Certified recyclers guarantee that hazardous materials are correctly handled, valuable resources are recovered efficiently, and no e-waste is irresponsibly exported to developing countries. This applies to individuals seeking a reliable recycling option and businesses managing large quantities of electronics.
Secure Your Data Before Disposal
E-waste often contains sensitive personal or corporate data. Whether it’s a smartphone, laptop, or external hard drive, securely wiping or destroying data is a non-negotiable step. Individuals can use software to erase personal files, while businesses may need to adopt professional-grade solutions. To ensure data security, many certified recyclers offer data destruction services, such as hard drive shredding or degaussing. This step is critical for businesses to meet compliance requirements for data protection laws like GDPR or HIPAA. Certified recyclers like 4THBIN also provide services that securely destroy HIPAA-compliant medical documents and X-rays.
Avoid Dumping or Burning Electronics
Dumping e-waste in landfills or burning it releases harmful chemicals like lead, mercury, and cadmium into the environment. These toxins can contaminate soil, water, and air, posing serious risks to ecosystems and human health. Both businesses and individuals should avoid these practices entirely. Instead, use designated recycling programs that prevent environmental damage and recover valuable materials from discarded electronics.
Reuse or Donate Functional Electronics
Before considering recycling, ask if your electronics can have a second life. Functional devices can be sold, donated, or refurbished, reducing waste and extending their usefulness. Individuals might donate old laptops to schools or nonprofits, while businesses can work with organizations that refurbish and distribute technology to underserved communities. This approach is not only sustainable but also socially beneficial.
Identify and Separate E-Waste by Type
Different types of e-waste require different disposal methods. Batteries, for instance, are hazardous and cannot be recycled with general electronics. Businesses should sort their e-waste by category—such as office equipment, batteries, and lighting—while individuals should ensure they are dropping off items at facilities equipped to handle their specific type of electronics. Sorting helps recyclers process materials more efficiently and safely.
Keep Records of E-Waste Disposal
For businesses, maintaining records of e-waste disposal is essential for audits, compliance with environmental laws, and demonstrating sustainability efforts. Certified recyclers often provide documentation showing how e-waste was handled. Individuals can also benefit from tracking their efforts as part of a personal commitment to responsible environmental practices.
Why Businesses Must Partner with Certified Recyclers
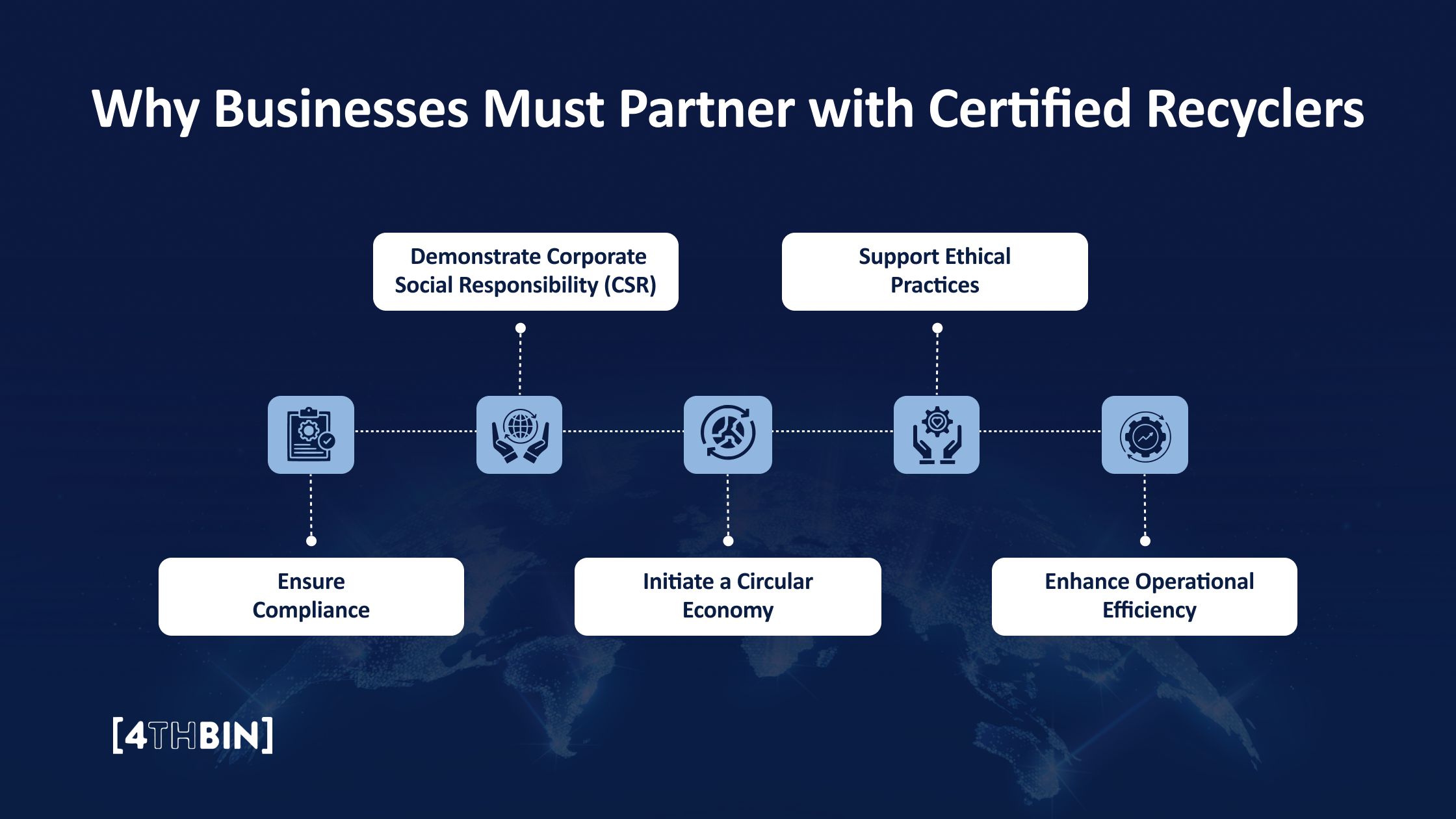
Managing e-waste is not just an operational challenge for businesses—it’s an ethical and strategic responsibility. Partnering with certified recyclers ensures that e-waste is handled responsibly, securely, and sustainably. Here’s why this partnership is essential:
Ensure Compliance
Governments are enforcing stricter regulations to address the growing e-waste crisis. State-specific e-waste regulations and laws in the U.S. require businesses to follow responsible disposal practices. Certified recyclers are experts in these regulations, ensuring your business avoids fines, legal issues, and reputational damage.
Demonstrate Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Businesses today are expected to lead the way in sustainability. Partnering with certified recyclers demonstrates your company’s commitment to ethical and environmentally friendly practices. By recycling responsibly, you contribute to reducing waste, conserving resources, and protecting global ecosystems, all of which resonate with environmentally conscious customers and stakeholders.
Initiate a Circular Economy
Certified recyclers play a vital role in the circular economy by recovering valuable materials like metals, plastics, and glass from e-waste and reintroducing them into production cycles. Partnering with these recyclers enables your business to contribute to a system that minimizes waste, extends the lifecycle of resources, and reduces reliance on raw material extraction. This aligns with sustainability goals and encourages innovation in manufacturing and design.
Support Ethical Practices
Not all recyclers operate ethically. Some engage in unethical practices, such as exporting e-waste to developing countries where unsafe recycling methods harm local communities and ecosystems. Certified recyclers follow strict ethical standards, ensuring e-waste is handled responsibly and without causing harm. Certifications like e-Stewards explicitly prohibit such harmful practices, giving businesses confidence that their e-waste is processed safely and ethically.
Enhance Operational Efficiency
Managing e-waste internally can be complex and time-consuming. Certified recyclers offer end-to-end solutions, including collection, transportation, sorting, and recycling. This streamlined process reduces the burden on your team, allowing your business to focus on its core operations while ensuring proper handling of e-waste.
Make E-Waste Management Effortless with 4THBIN

Choosing a certified recycler is no longer optional; it’s essential for ensuring compliance, safeguarding sensitive data, and minimizing environmental impact. With 4THBIN ’s e-recycling solutions, your organization can rest assured of secure, compliant, and environmentally responsible electronic waste disposal.
With over a decade of experience, 4THBIN has partnered with more than 10,000 organizations, including Fortune 100 companies and small businesses, to transform e-waste challenges into opportunities. We make the process seamless, offering businesses a way to turn a potential liability into an opportunity for leadership in sustainability and responsibility.
Our certified data destruction services ensure that sensitive information is completely safeguarded, eliminating the risks of data recovery associated with improper disposal. From secure RemoteReturn mail-in options to convenient on-site collection, our customizable solutions allow you to choose the plan that best suits your organization’s needs.
Responsible E-Waste Recycling Starts Here.










